Wound care is an important topic to discuss in conjunction with syringe services programs (SSPs) and other harm reduction practices. Those who inject drugs are at a higher risk of infection. For information about the serious health considerations for individuals and implications for healthcare systems, please see below.
Soft Tissue Infections
Wound care is an important issue for people who inject drugs (PWID). The body of literature shows that people who inject drugs are at an increased risk of soft tissue infections including cellulitis and abscesses2. Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection whose symptoms include redness, pain, rash, tight skin, feeling of warmth, and fever5. Abscesses are characterized by the same symptoms as cellulitis, with some exceptions in presentation1. If a patient presents with any of these symptoms and is someone who injects drugs, they should seek the care of a medical provider1.
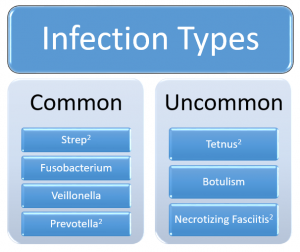
Skin infections are the cause of a large amount of health care expenses and hospitalizations in the PWID population. The literature notes that this population as at risk for both common and uncommon infections2.